- SnapLogic - Integration Nation
- Designing and Running Pipelines
- Re: How to create timestamps and out put them only...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-29-2024 07:03 AM
I need to generate timestamps using Script snap for Python. I tried to use datetime and java.sql.Timestamp but Type Inspector recognizes them as java.util.LinkedHashMap and the operator instanceof returns false for DateTime and LocalDateTime. Is it possible to generates timestamp only using Python?
Thanks in advance
Solved! Go to Solution.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-29-2024 09:26 AM
@tlikarish Thanks for sharing this. In your case you are adding Mapper.
I found another solution the script already returns the LocalDateTime data type. In the case I can generate time ranges using only Python.
# Import the interface required by the Script snap.
from com.snaplogic.scripting.language import ScriptHook
from java.util import LinkedHashMap
from org.joda.time import DateTime, LocalDateTime, LocalDate, LocalTime
class TransformScript(ScriptHook):
def __init__(self, input, output, error, log):
self.input = input
self.output = output
self.error = error
self.log = log
# The "execute()" method is called once when the pipeline is started
# and allowed to process its inputs or just send data to its outputs.
def execute(self):
self.log.info("Executing Transform script")
while self.input.hasNext():
# Read the next document, wrap it in a map and write out the wrapper
in_doc = self.input.next()
out_doc = LinkedHashMap()
out_doc.put("DateTime", DateTime.now())
out_doc.put("LocalDateTime", LocalDateTime.now())
out_doc.put("LocalDate", LocalDate.now())
out_doc.put("LocalTime", LocalTime.now())
self.output.write(out_doc)
self.log.info("Finished executing the Transform script")
# The Script Snap will look for a ScriptHook object in the "hook"
# variable. The snap will then call the hook's "execute" method.
hook = TransformScript(input, output, error, log)
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-29-2024 08:49 AM
Hi Palermo,
Here are some examples of how timestamps can be used within a Script snap. See the attached pipeline if you want to try it out.
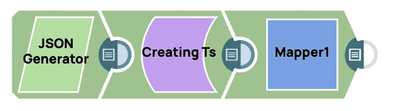
This segment of the pipeline shows one way to create a Timestamp from within the Python Script snap using the Java Instant class and passing the value to a downstream Mapper that will parse it back into a compatible Date type.
#Import the interface required by the Script snap.
from com.snaplogic.scripting.language import ScriptHook
from java.time import Instant
class TransformScript(ScriptHook):
def __init__(self, input, output, error, log):
self.input = input
self.output = output
self.error = error
self.log = log
# The "execute()" method is called once when the pipeline is started
# and allowed to process its inputs or just send data to its outputs.
def execute(self):
self.log.info("Executing Transform script")
while self.input.hasNext():
try:
# Read the next input document, store it in a new dictionary, and write this as an output document.
inDoc = self.input.next()
outDoc = {
'original' : inDoc,
'ts': Instant.now().toEpochMilli()
}
self.output.write(inDoc, outDoc)
except Exception as e:
errDoc = {
'error' : str(e)
}
self.log.error("Error in python script")
self.error.write(errDoc)
self.log.info("Script executed")
# The "cleanup()" method is called after the snap has exited the execute() method
def cleanup(self):
self.log.info("Cleaning up")
# The Script Snap will look for a ScriptHook object in the "hook"
# variable. The snap will then call the hook's "execute" method.
hook = TransformScript(input, output, error, log)
I included another segment in the pipeline that shows the opposite, eg. how to create a timestamp in the Mapper, then use it within a Script snap. I don't think that's exactly what you were after, but hopefully it may help others in their work.
Hope this helps you.
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
03-29-2024 09:26 AM
@tlikarish Thanks for sharing this. In your case you are adding Mapper.
I found another solution the script already returns the LocalDateTime data type. In the case I can generate time ranges using only Python.
# Import the interface required by the Script snap.
from com.snaplogic.scripting.language import ScriptHook
from java.util import LinkedHashMap
from org.joda.time import DateTime, LocalDateTime, LocalDate, LocalTime
class TransformScript(ScriptHook):
def __init__(self, input, output, error, log):
self.input = input
self.output = output
self.error = error
self.log = log
# The "execute()" method is called once when the pipeline is started
# and allowed to process its inputs or just send data to its outputs.
def execute(self):
self.log.info("Executing Transform script")
while self.input.hasNext():
# Read the next document, wrap it in a map and write out the wrapper
in_doc = self.input.next()
out_doc = LinkedHashMap()
out_doc.put("DateTime", DateTime.now())
out_doc.put("LocalDateTime", LocalDateTime.now())
out_doc.put("LocalDate", LocalDate.now())
out_doc.put("LocalTime", LocalTime.now())
self.output.write(out_doc)
self.log.info("Finished executing the Transform script")
# The Script Snap will look for a ScriptHook object in the "hook"
# variable. The snap will then call the hook's "execute" method.
hook = TransformScript(input, output, error, log)
- Remove XML duplicate key from JSON list in XML formatter in Designing and Running Pipelines
- CSV parser cannot parse data in Designing and Running Pipelines
- Parsing XML using a Python script returns an encoding error message in Designing and Running Pipelines
- Mapper strange behaviour when using jsonpath to get array and sink to Snowflake in Designing and Running Pipelines
- Generic JDBC Execute snap with complex DB2 SQL -> ran into "Connection does not exist" Error in Snap Packs